Understanding the 95th Percentile Bandwidth Billing: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of data centres and network providers, bandwidth billing is a critical aspect that often confuses many customers. One prevalent method used for billing is the 95th percentile bandwidth billing. This article aims to demystify this concept, explain its advantages, and illustrate how it impacts your internet costs.
What is 95th Percentile Bandwidth Billing?
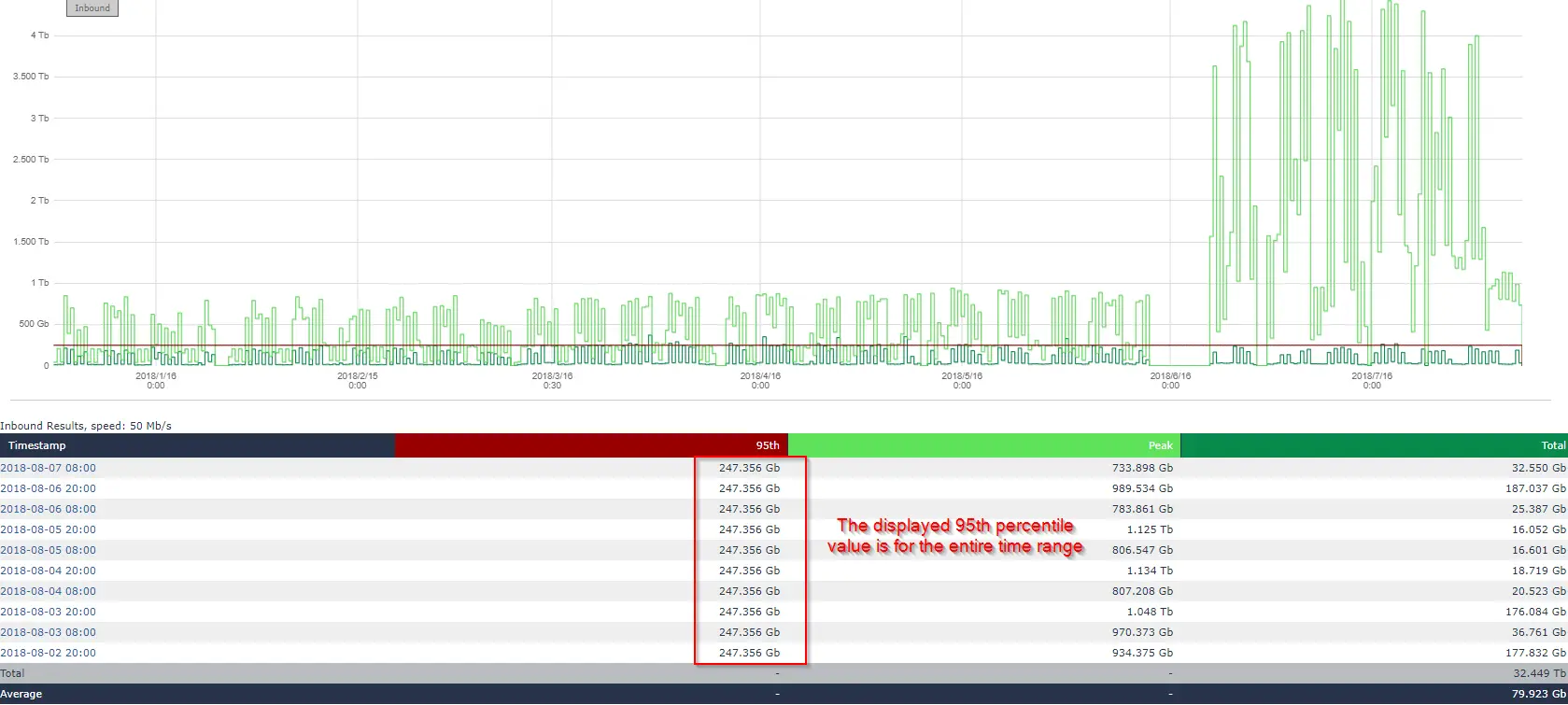
The 95th percentile bandwidth billing is a method used by data centres to measure and bill for data usage. Instead of charging for every bit of data transferred, this method focuses on the peak usage times. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Data Collection: Throughout the billing cycle (usually a month), the data centre collects data points representing your bandwidth usage at regular intervals, typically every 5 minutes.
- Sorting Data: These data points are then sorted in ascending order.
- Excluding Top 5%: The top 5% of the data points are discarded. This means the highest 36 hours of usage in a month (for 5-minute intervals) are not considered.
- 95th Percentile Point: The value at the 95th percentile is then used to determine your bill. This value represents your peak usage, excluding occasional spikes.
Why Use the 95th Percentile Method?
The 95th percentile method is favoured for several reasons:
- Simplicity and Fairness: It avoids charging for short-term spikes that might occur due to unusual events, thus providing a fairer billing system.
- Encourages Efficient Usage: Users are incentivised to manage their bandwidth efficiently, as consistent high usage will be reflected in their billing.
- Predictable Costs: This method offers more predictable costs for both providers and customers compared to flat-rate or total data transfer billing.
Calculating the 95th Percentile Bandwidth
Let’s consider a simple example to illustrate how this calculation works:
- Suppose your data centre collects data every 5 minutes, resulting in 8,640 data points in a 30-day month (24 hours * 60 minutes / 5 minutes * 30 days).
- After sorting these data points, the top 5%, which is 432 data points (8,640 * 0.05), are discarded.
- The highest value from the remaining 8,208 data points (8,640 – 432) is considered the 95th percentile value.
This value is then used to determine your billing. For instance, if your 95th percentile value is 100 Mbps and your contract rate is £1 per Mbps, your monthly bill would be £100.
Advantages of 95th Percentile Billing
- Cost Efficiency: By not charging for peak spikes, this method can be more cost-effective than other billing methods.
- Scalability: It scales well with varying usage patterns, making it suitable for businesses with fluctuating bandwidth demands.
- Performance Monitoring: It provides a clear metric for monitoring network performance and planning capacity.
Potential Drawbacks
While the 95th percentile method has many advantages, it also has some potential drawbacks:
- Complexity: Understanding and predicting the 95th percentile value can be complex for some users.
- Unexpected Costs: Sudden changes in usage patterns can still lead to higher bills if not managed properly.
Tips for Managing 95th Percentile Bandwidth Billing
- Monitor Your Usage: Regularly monitor your bandwidth usage to identify peak times and manage them effectively.
- Optimise Network Traffic: Use network optimisation techniques to distribute traffic more evenly and avoid high peaks.
- Plan for Growth: Consider future growth and potential usage increases to ensure your bandwidth plan can accommodate changes without significant cost increases.
The 95th percentile bandwidth billing method offers a balanced approach to managing internet costs, particularly for businesses with variable data usage patterns. By understanding how it works and implementing strategies to manage your usage, you can take full advantage of this billing method while keeping your costs under control.
Understanding and leveraging the 95th percentile method can lead to more predictable and often lower internet expenses, making it a valuable tool for any organisation relying heavily on data transfer.